Transport and optical characterization of CZTS thin film solar cells
Objective
- Study of defect physics: a deeper understanding of the fundamental properties of CZTS, particularly the nature of the defects as well as their impact on the properties of CZTS material is important for further improvement the efficiency of CZTS solar cells.
- Band gap engineering: band gap tuning via substitution of Sn by Ge and/or S by Se can control the band gap of CZTS thin film. The widening effect of band gap through Ge incorporation and the narrowing effect of band gap through Se incorporation facilitate the design of high efficiency CZTS thin film solar cell based on multi-junction.
Approach
We plan to employ various methods to study the defects properties and the effectiveness of band gap tuning. These include temperature dependent and time resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy, temperature and magnetic field dependent resistance and Hall resistance measurements, and temperature dependent photo-conductance spectroscopy.
Impact
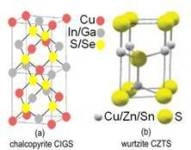
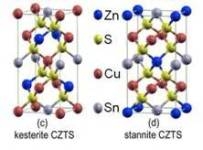
- Quaternary compound Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films are very promising candidate for high efficiency, low cost, non-toxic and rare metal-free solar cells.
- CZTS is a compound semiconductor of (I)2(II)(IV)(VI)4. It has a high absorption coefficient (> 104 cm-1) and a desirable band gap (~1.45 eV) and it has been theoretically predicted that its conversion efficiency can be as high as 32%.
- A thorough understanding of the properties of CZTS material is important for further improvement the efficiency of CZTS solar cells.
Contact
Jiannong Wang, Professor of Physics
Email: phjwang@ust.hk